IPAWS G7-04
Description
The computation is based on the parameters provided by the technical report G7-04
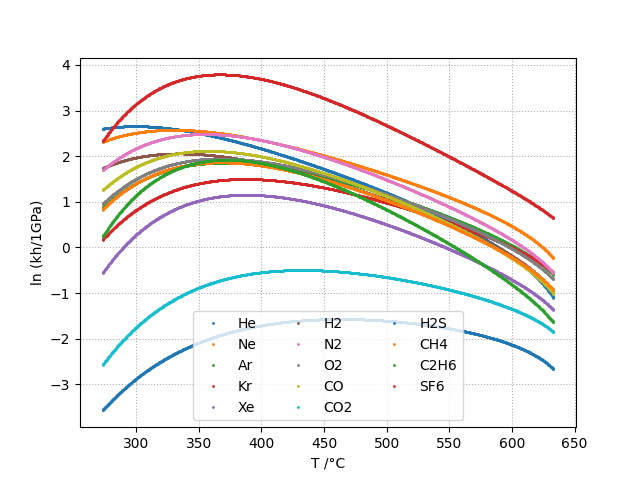
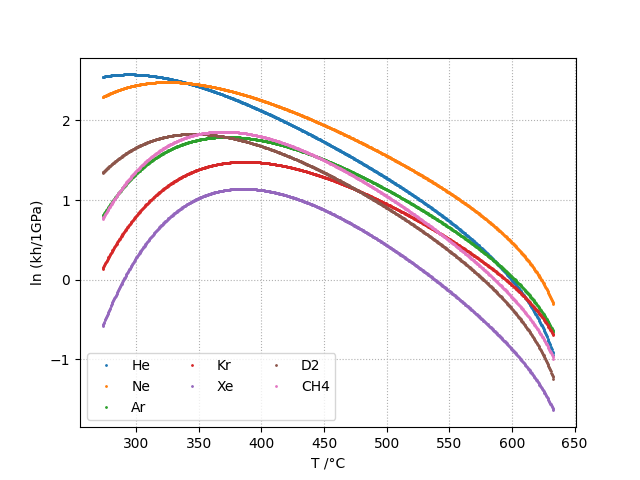
Henry Contant: kh
The Henry constant is defined as shown in equation below. kh is expressed in MPa.
- : liquid-phase fugacity
- : mole fraction of the solute
The Henry’s constant kh is given as a function of temperature by:
- : critical temperature of the solvent as recommended by IAPWS.
- is the vapor pressure of the solvent at the temperature of interest and is calculated from the correlation of Wagner and Pruss for and from the correlation of Harvey and Lemmon for .
Both equations have the form:
- is 6 for and 5 for
- is the critical pressure of the solvent recommended by the report R2-83
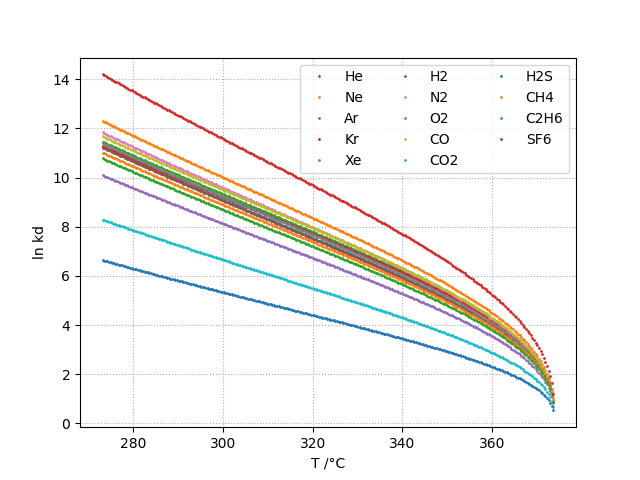
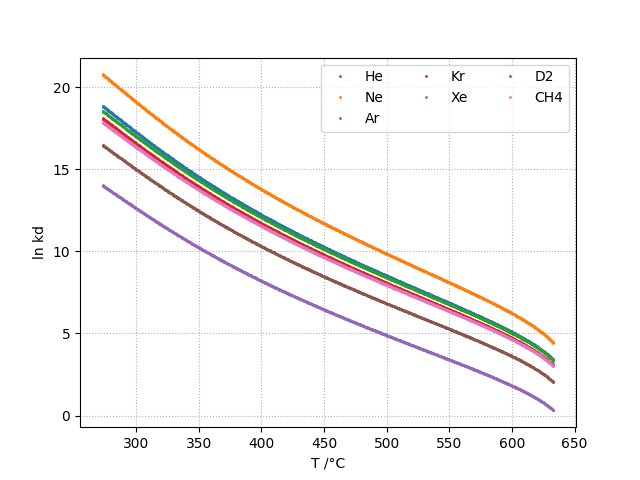
Vapor-Liquid Distribution Constant: kd
The liquid-vapor distribution constant kd is defined as shown in equation below. kd is adimensional.
- : mole fraction of the solute
- is the vapor-phase solute mole fraction in equilibrium with the liquid
The vapor-liquid distribution constant kd is given as a function of temperature by:
- : -0.023767 for and -0.024552 for .
- Wagner et al. for and fernandez-prini et al. for
In both cases, has the following form:
- is 6 for and 4 for
Molar fractions
The molar fractions and as following:
By fixing at 1.0 it comes that the molar fractions and are then expressed per unit of pressure as shown in the following equation .
The molar fractions can be converted to solubilties in ppm or cm3/kg by considering dilute solutions. is the considered gas and the solvent is either or .
Available gases
kh and kd can be computed for the following gases:
- in water: He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, H2, N2, O2, CO, CO2, H2S, CH4, C2H6, SF6
- in heavywater: He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, D2, CH4
The available gases can be retrieved with
- gases which returns the available gases as a list.
- gases2 which return the available gases as a string.
- ngases which returns the number of available gases.
Plots